JDBC Architecture and Components Explained
JDBC is an API that helps applications communicate with databases. It allows Java programs to connect to a database, run queries, retrieve, and manipulate data. Because of JDBC, Java applications can easily work with different relational databases like MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, and more.
JDBC Architecture
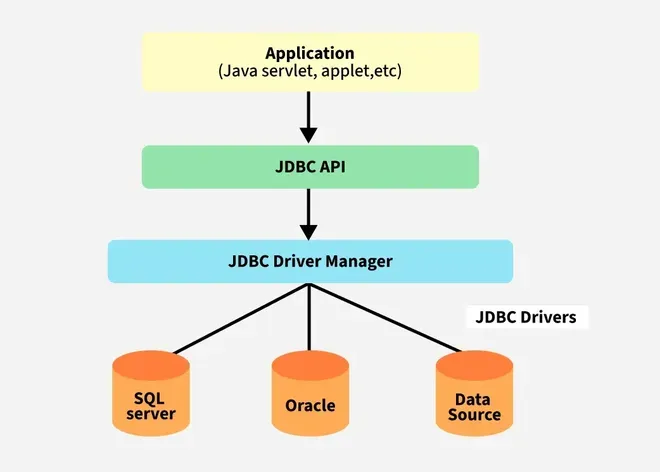
Components of JDBC Architecture
Explanation of Components
- Application: This can be a Java application or servlet that communicates with a data source.
- The JDBC API: It allows Java programs to execute SQL queries and get results from the database. Some key components of the JDBC API include:
- Interfaces like
Driver,ResultSet,RowSet,PreparedStatement, andConnectionthat help manage different database tasks. - Classes like
DriverManager,Types,Blob, andClobthat help manage database connections.
- Interfaces like
- DriverManager: It plays an important role in the JDBC architecture. It uses database-specific drivers to effectively connect enterprise applications to databases.
- JDBC Drivers: These drivers handle interactions between the application and the database.
The JDBC architecture consists of two-tier and three-tier processing models to access a database. They are described below:
1. Two-Tier Architecture
A Java Application communicates directly with the database using a JDBC driver. It sends queries to the database, and the result is then sent back to the application. For example, in a client/server setup, the user’s system acts as a client that communicates with a remote database server.
Structure:
Client Application (Java) -> JDBC Driver -> Database
2. Three-Tier Architecture
In this model, user queries are sent to a middle-tier service, which interacts with the database. The database results are processed by the middle tier and then sent back to the user.
The 4 Main Components of JDBC
There are generally 4 main components of JDBC through which it can interact with a database. They are mentioned below:
1. JDBC API
It provides various methods and interfaces for easy communication with the database. It includes two key packages:
java.sql: This package, part of Java Standard Edition (Java SE), contains the core interfaces and classes for accessing and processing data in relational databases. It also provides essential functionalities like establishing connections, executing queries, and handling result sets.javax.sql: This package is part of Java Enterprise Edition (Java EE), which extends the capabilities ofjava.sqlby offering additional features like connection pooling, statement pooling, and data source management.
The JDBC API also provides a standard way to connect a database to a client application.
2. JDBC Driver Manager
Driver Manager is responsible for loading the correct database-specific driver to establish a connection with the database. It manages the available drivers and ensures the right one is used to process user requests and interact with the database.
3. JDBC Test Suite
It is used to test the operations (such as insertion, deletion, and updating) being performed by JDBC Drivers.
4. JDBC Drivers
JDBC drivers are client-side adapters (installed on the client machine, not on the server) that convert requests from Java programs to a protocol that the DBMS can understand. There are 4 types of JDBC drivers:
- Type-1 driver or JDBC-ODBC bridge driver
- Type-2 driver or Native-API driver (partially Java driver)
- Type-3 driver or Network Protocol driver (fully Java driver)
- Type-4 driver or Thin driver (fully Java driver) – It is a widely used driver. The older drivers like the JDBC-ODBC bridge driver have been deprecated and are no longer supported in modern versions of Java.
