Human Sensory Organs and Nervous System Health
The Senses of Hearing
Health of Sensory Organs
Vision Disorders
- Short-sightedness (Myopia): Distant objects appear out of focus because the eyeball is too long, causing images to focus *in front of* the retina. Concave lenses or surgery can correct this.
- Long-sightedness (Hypermetropia): Close objects appear out of focus because the eyeball is too short. This causes images to focus *behind* the retina. Convex lenses or surgery can correct this.
- Astigmatism: Objects appear distorted or blurred. It is caused by an irregularly shaped cornea. Lenses or surgery can correct the problem.
- Cataracts: The crystalline lens loses its transparency until it becomes opaque. This causes progressive vision loss and possible blindness.
- Conjunctivitis: An inflammation of the conjunctiva, usually caused by an infection or allergy.

Typical Disorders of the Skin, Ear, and Nasal Passages
Organ | Disorders | Description and Causes |
Skin | Urticaria (Hives) | A rash or welt caused by an allergic reaction to food or medicine. |
Psoriasis | A chronic condition that produces thick red skin with silver scales. | |
Ear | Otitis | An acute or chronic inflammation usually caused by infection. |
Deafness | Hearing loss. It may be genetic or caused by diseases or trauma. | |
Nasal Cavities | Rhinitis | Inflammation of the nasal respiratory membrane, often caused by allergies. It causes nasal congestion, sneezing, etc. |
Health Habits for Sensory Organs
Eat a healthy diet. Avoid the use of harmful substances. Have routine examinations. Maintain good hygiene and avoid injuries.
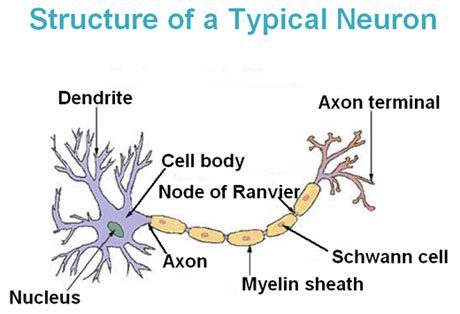
Components of the Nervous System
The neurons function includes: Sensory neurons, Motor neurons, and Relay neurons.
Transmission of Nerve Impulse
The presynaptic neuron transmits the impulse; it travels through the axon. The postsynaptic neuron receives the impulse and sends it to the axon terminals.
Synapse Components
Neurotransmitters, Synaptic cleft, Receptors (postsynaptic neuron).
Responses of the Somatic Nervous System
Voluntary Response Pathway
- The stimulus is detected by a receptor.
- The stimulus is transmitted by the optic nerve to the brain.
- The brain interprets the stimulus and responds.
- The response is transmitted as a nerve impulse from the brain through a motor nerve to the muscles.
- The muscles carry out the response.
Involuntary Response Pathway
- The stimulus is detected by a receptor.
- Sensory neurons transmit nerve impulses to the spinal cord.
- A relay neuron in the spinal cord connects the sensory neuron to the motor neuron.
- The motor neuron carries the response to a muscle.
- The muscle carries out the response.
Health of the Nervous System
Disorders include: Infectious diseases, Cerebrovascular events, Physical trauma, and progressive neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s).
Mental Health Conditions
- Phobias: A disorder due to a persistent, irrational fear (e.g., fear of small places).
- Dementia: A disease characterized by declining brain function. Symptoms include problems with memory, language, and even identity. Causes are varied: injury, disease, aging, etc.
- Depression: A mood disorder that interferes with daily life. Symptoms vary: sadness, low self-esteem, negative, and suicidal thoughts.
- Schizophrenia: A brain disorder that appears in adolescence or adulthood. Symptoms include hallucinations and drastic changes in behavior.
Healthy Habits for the Nervous System
Maintain an orderly life. Exercise. Develop social relationships. Perform intellectual activities regularly. Take protective measures to prevent injury. Avoid smoking, drinking alcohol, or using drugs (Drugs and Health): Stimulants, Depressants, Mind-altering substances, Tolerance, Dependence.